Your domain name is more than just a web address; it’s a crucial part of your brand identity. Whether you’re publishing a blog, showcasing a portfolio, or starting an online store, a domain name is often the first thing potential customers encounter, making it an essential part of your online presence.
Taking the time to choose the right domain name is critical for long-term success. A well-chosen domain name can boost brand recognition and make it easier for customers to find you online. Conversely, switching domain names after launch can harm your search engine rankings and confuse customers.
This guide will walk you through how to register a domain name, offering expert advice on choosing the perfect web address for your business.
How to Register a Domain Name in Six Steps
1. Choose a Domain Name
Your domain name is a key part of your brand identity. If you’re still in the process of naming your business, consider the domain name as part of that decision. A domain name that matches your brand name will be easier for customers to remember.
If you already have a business name, your preferred domain name might be YourBrand.com. But what if it’s already taken? Don’t worry—you have options:
- Use a suffix: Differentiate your domain name by adding a word to the end. This could be your main product (YourBrandShoes.com), your location (YourBrandCanada.com), or something all-encompassing (YourBrandOnline.com).
- Use a prefix: Start your domain name with an action-oriented verb that highlights your product or service (GetYourBrand.com, WearYourBrand.com, EatYourBrand.com).
- Try a different domain extension: While .com is the most commonly used top-level domain (TLD) extension, there are plenty of alternatives. You could use a region-specific extension (like .uk or .ca) or a specialized extension (like .shop or .store). Keep in mind that specialized extensions often come with a higher price tag.
Use a free domain name generator to brainstorm business names and check domain name availability instantly.
2. Check Domain Name Availability
Checking to see if your chosen domain name is available is quick and easy. Most web hosting services offer free domain name search tools that tap into a record system called WHOIS or RDAP.
Keep in mind, domain names are universal. If a domain name isn’t available from one provider, it’s not available from any other provider either.
3. Choose a Domain Registrar
A domain registrar is a company that registers domain names on your behalf. When you purchase a domain name, the registrar adds it to the Domain Name System (DNS) for you.
You can purchase domain names from a variety of different businesses:
- Website building platforms (like Shopify, Squarespace, or WordPress)
- Web hosting services (like HostGator or Bluehost)
- Dedicated domain registrars (like GoDaddy or NameCheap)
Domain names are typically paid for on a recurring basis, usually annually, rather than as a one-time purchase.
When choosing a domain name provider, consider the following factors:
- Ease of use: How simple will it be to connect your domain name to your website?
- Privacy protection: When you register a domain name, your contact information is made public in the global ICANN registry. Domain privacy protection will hide this information.
- Available domain extensions: If you’re interested in a region-specific domain extension (such as .uk or .ca) or a specialized extension (like .shop or .store), make sure the provider you choose offers it.
- Additional services: Many domain registrars offer additional services like e-commerce hosting, website building tools, and email hosting.
4. Purchase and Register Your Domain Name
Once you’ve chosen a registrar and decided on your domain name, you’re ready to make a purchase.
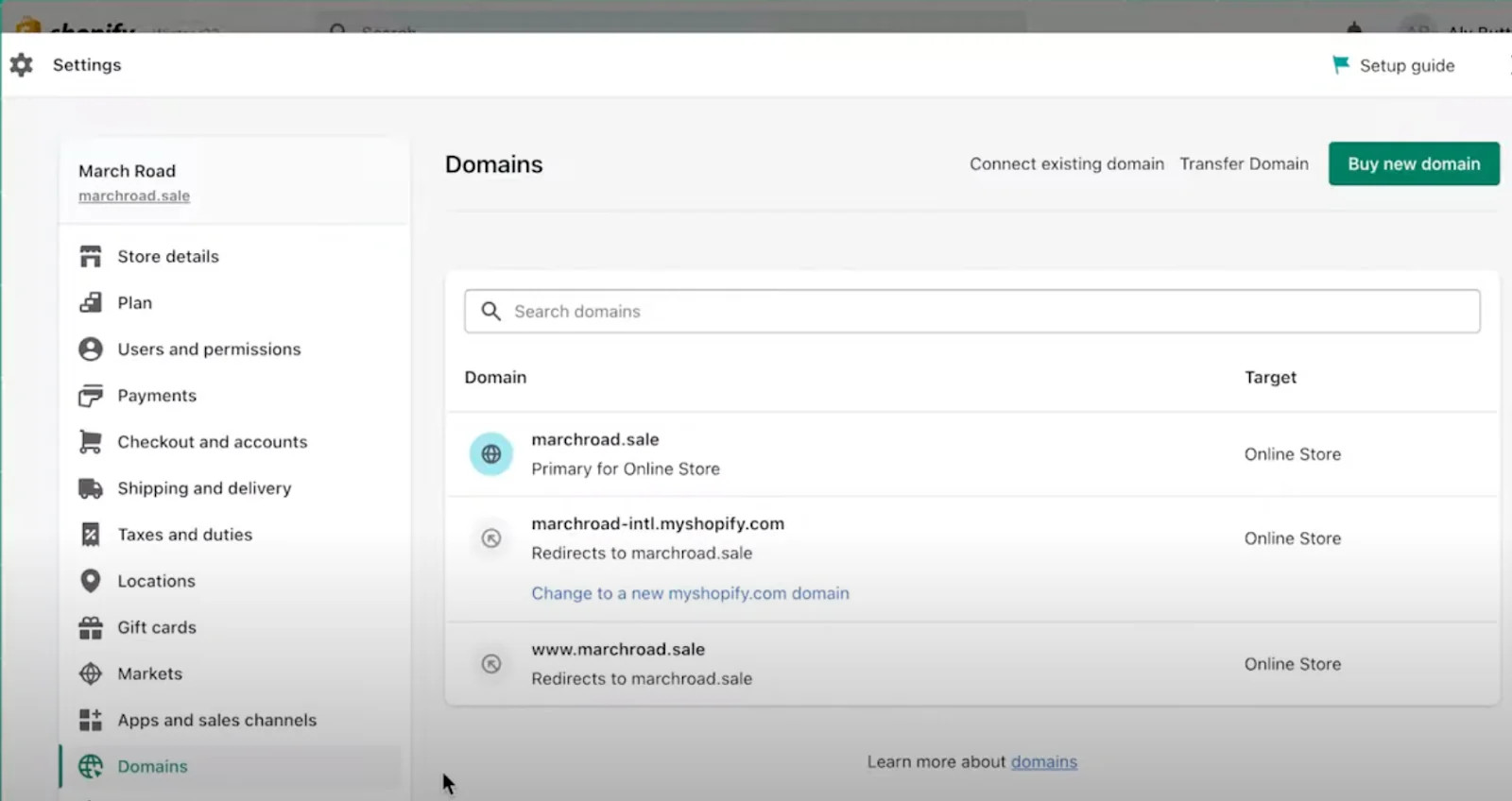 Screenshot of the Shopify domains tab showing the primary domain and redirected domains for an online store.
Screenshot of the Shopify domains tab showing the primary domain and redirected domains for an online store.
Note that it can take up to 48 hours for your new domain name to become fully active.
5. Review Your Domain Name Agreement
Before finalizing your domain name purchase, carefully read the registrar’s terms and conditions. The domain name agreement is a legally binding document that outlines:
- Who has full ownership of the domain name
- Renewal terms and associated fees
- Additional costs for services like domain name restoration or privacy protection
- Conditions for transferring the domain name to another provider
- Payment terms, including the consequences of missed payments
6. Renew Your Domain Name
When you purchase a domain name, you’re securing it for a fixed period, usually one year. To maintain ownership of your domain name, you’ll need to renew it when your term expires. Most domain name providers offer auto-renewal, which is generally recommended.
Keep in mind that if your payment information changes, you’ll need to update your settings with your domain provider so they can charge you for the auto-renewal.
If you fail to renew your domain name, it will no longer direct to your website and could be purchased by someone else.